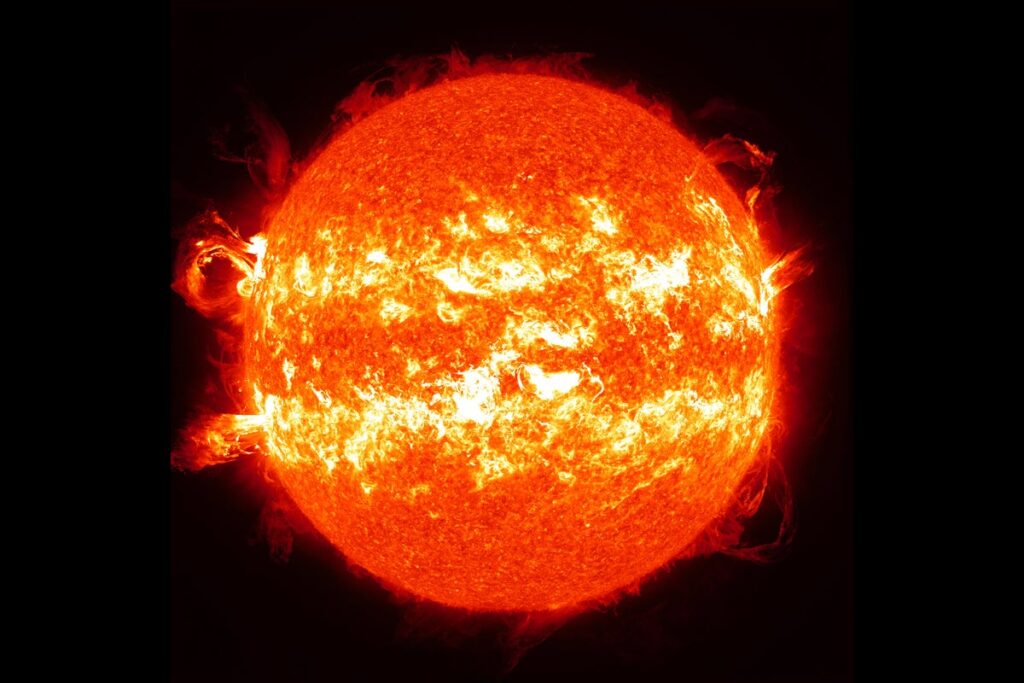
The sun can be entering a stronger 11 -year cycles
The Sun has produced impressive auroras on Earth in recent years as the solar activity has reached its maximum point, but expects more in the coming years
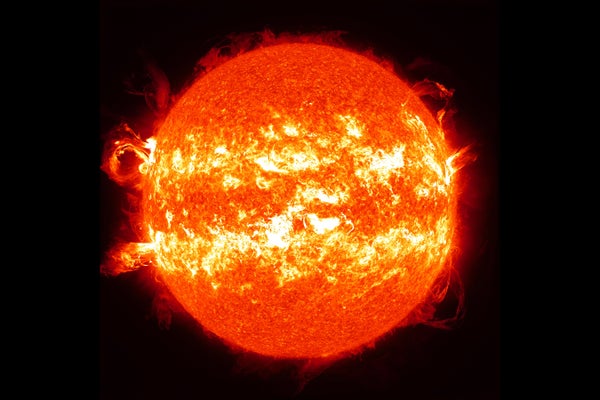

Mass solar flares, elegant eruptions of solar material and a huge sunscreen constitute some of the images captured by the NASA Dynamics Solar Observatory in 2013 and 2014.
NASA/SD/S Goddard Space Flight Center. Wiessinger
A year ago this weekend, the activity of the Sun created some of the most spectacular auroras registered, with visible exhibitions to southern Florida.
The incredible shows last May (and another auroral outbreak last October) were partly a matter of luck because several factors, some of them serendiposous, affect the appearance of Aurora. But the sun had prepared to present a show, since it approached the maximum phase of its 11 -year activity cycle, and that high activity continues today. This solar cycle still has the potential to cause more celestial glasses before the activity is calmed. And scientists say that the next solar cycles can be even more agitated. But it is still quite difficult to apply the behavior of the sun.
“Solar storms: it is something probabilistic, so sometimes they do not always do what you would expect,” says Lisa Upton, heliophysics of the Southwest Research Institute.
About support for scientific journalism
If you are enjoying this article, consider support our journalism awarded with Subscription. When buying a subscription, it is helping to guarantee the future of shocking stories about the discoveries and ideas that shape our world today.
The sun right now
The sun is essentially a massive liquid magnet. Heliophysicists evaluate the activity of our star by counting the amount of sun spots, relatively “cold” clubs of their magnetic field that are from the source of radiation and plasma bursts, on its surface. (Scientists monitor this real -time count, but evaluate the internships of the solar cycle based on the soft. Therefore, the formal statement of the maximum and minimum of a cycle always always shells after the fact).
The number of sun spots rises and is reduced naturally about 11 years, the magnetic posts of the sun first strengthen, then weaken and finally turn. When the magnetic field of the sun is quieter, with a post that is firmly positive and that is firmly negative, the activity is minimal, since it was more recently around December 2019, and the star is sometimes completely free of imperfections.
For more than a year, the sun has been in the opposite phase, the solar maximum, with a messy magnetic field, many sunscreen and regular outbursts. August 2024 produced most of the sun spots of any recent month, with more than 200 storms of this type.
Since then, sun spots have become less numerous, but it is not yet clear if the maximum solar is really coming out. “We have had a little deceleration in the activity [during] The last two months. That is not too surprising, “says Upton.” One question at this point, which will be interesting, is whether or not we have another small peak in the activity. “
She says that if such a spike happened, it would probably reach about three months, reflecting a small spike that occurred in June and July 2023. “But the sun likes to surprise us,” Upton adds. “
Long -term cycles
Like scientists, they observe how the current solar cycle develops, they are also working to understand what future cycles could bring.
That is a difficult task, since modern science is only in the 25 activity cycle in which researchers have made abundant observations of sunscreen. The most sophisticated observations that help scientists understand the sun in detail, such as spatial observations and magnetic data, are even dog, and some offer information about only a couple of solar cycles so far. Scientists can study tree rings and ice nuclei to obtain a basic sensation of solar activity before the observations are broken, but the thesis data is less detailed and do not provide precise sunscreen counts.
A hypothesis suggests that the sun shows a longer-term variability called Gleissberg cycle, named for the Wolf Gelissberg astronom about 2,400 years). And a new analysis of protons Earthe Bestbertbert Bertberged Be started.
Not all heliophysics are sold in the Gleissberg cycle, Howver, since scientific data scientists have to work. “It is a child or debatable whether or not it is a physical phenomenon versus a statistical phenomenon,” says Upton.
Anyway, it is very likely that the duration of the next solar cycles, the sun will be more active than bone in the last two decades. This is because Solar Cycle 24, which dominated 2010, was one of the weakest recorded, and the current cycle has remained below the average in the activity.
“We, as humans, have little memory, and many people have amazed and astonished by what is happening in the last year or two in the sun,” says Upton. “There is this tendency to forget this longer term variability in what the sun is doing.”
Why does it matter
Sun’s activity not only paints our skies with spectacular dawn. Radiation and plasma bursts emitted by the sun can have real consequences for terrestrial life: solar storms can interfere with orbit satellites, including communication and navigation infrastructure, and serious incidents can even affect the electricity network on the ground.
And if our technology is vulnerable to the set of phenomena collectively called space climate, human bodies are even more. Fortunately, people on the surface of the earth are well protected from the activity of the sun by a magnetic bubble that surrounds our planet and deviates the great of the most dangerous emissions.
However, the risks of solar activity extend through the solar system. As NASA and other space agencies seek to send humans beyond orbit, the Mars already Mars, these organizations will need to protect astronauts from the hazards of the space climate, work that will include better predictions of which external regions.
“As the activity of the solar cycle increases, and it is very likely that we are in weaker than three cameras, it will become increasingly important to understand the space climate not only in the direction of the earth.
]